Lyme Disease
Total Antibody Immunoassay
What is Lyme Disease?

Lyme Disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected blacklegged tick. Lyme disease is the most reported vector-borne illness in the United States, and cases have been reported in all 50 states. The symptoms of Lyme Disease are highly variable and similar with those of several other diseases. The most common symptoms of Lyme Disease are fever, headache, fatigue, joint pain and reduced mobility, muscle pain, along with cognitive problems. However, most people associate the contraction of Lyme Disease with the development of a bulls-eye rash (clinically referred to as erythema migrans).
Includes:
If Lyme Disease Antibody is Positive or Equivocal (≥0.91), then Lyme Disease Supplemental Antibodies (IgG, IgM), Immunoassay will be performed at an additional charge (CPT code(s): 86617 (x2)).
Sample Requirement:
Serum, 3.5mL volume. Container: Glass or plastic red-top tube or SST.
Product Handling:
Ship at ambient temperature overnight. Stable 14 days room temperature, refrigerated, frozen.
New Paradigm in Lyme Disease Testing

The diagnosis of Lyme Disease is often delayed because the symptoms can be mistaken for other diseases, and because until recently the gold-standard, CDC-recommended testing protocol involved a primary immunoassay screen followed by a western blot confirmatory test.
This standard two-tier test (STTT) is considered only 50% accurate- very poor performance for a clinical test of such great importance to patient health. This paradigm shifted with the FDA-clearance of the Modified two-tier-tests (MTTT™) by Zeus Scientific in 2019. These tests can detect up to 30% more acute/early Lyme cases compared with the STTT.
Incite Health is proud to be offering the Zeus Scientific MTTT algorithm test under our CLIA-certification/ CAP-accreditation to support highly sensitive and specific testing for Lyme disease.
ZEUS Borrelia MTTT Advantages

Reduces the number of false clinically negative patient samples. Significantly improved sensitivity in the detection of IgG and IgM antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in early Lyme disease is achieved.
Affords Rapid Turn-Around-Time to rapid therapeutic intervention.
Completely eliminates the subjectivity of western blot interpretation.
Provides enhanced confidence in diagnostic assessment. As a first-tier test, The ZEUS ELISA™ Borrelia VlsE1/pepC10 IgG/IgM Test System is more clinically sensitive when compared to single antigen tests for detecting acute disease.
ZEUS Borrelia MTTT-2™
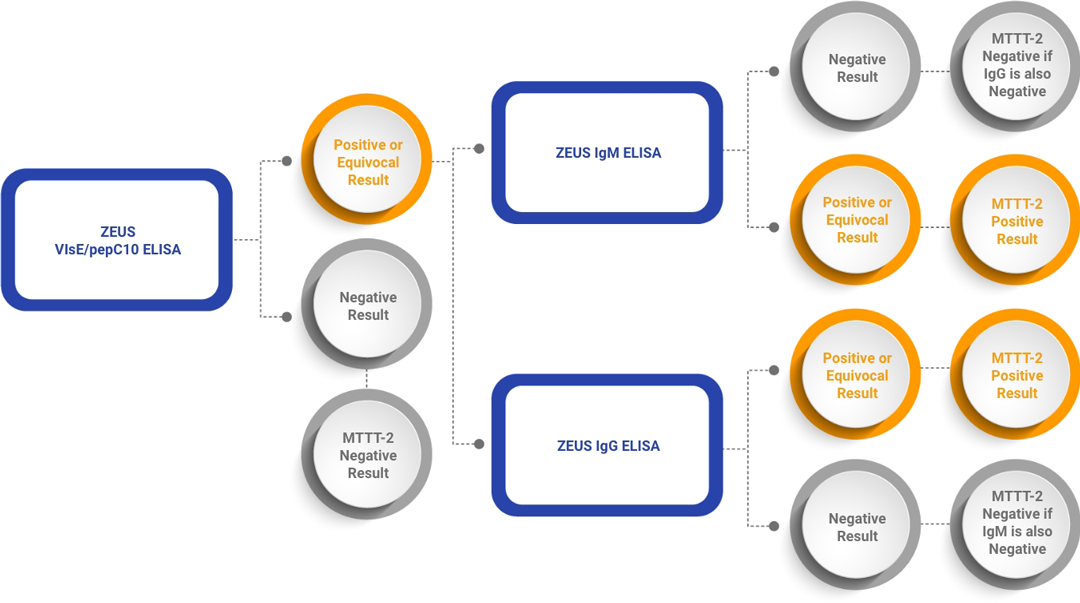
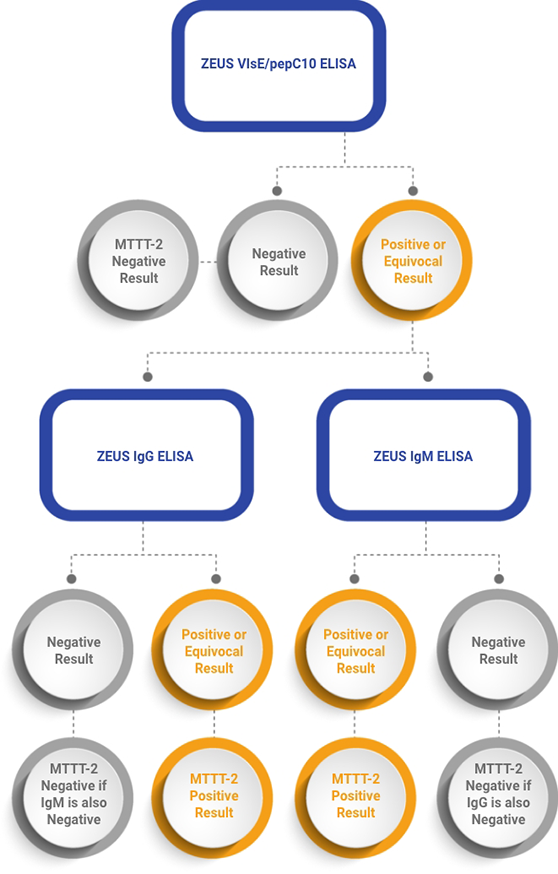
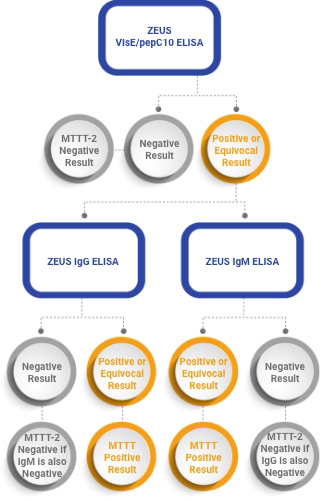
Summary of the Zeus Scientific MTTT-2 Clinical Testing Protocol offered by Incite Health. MTTT-2 uses a VlsE1/pepC10 polyvalent ELISA as the initial screen, followed by separate second tier IgG and IgM confirmatory ELISAs; this delivers the highest sensitivity for early detection of Lyme without compromising specificity.
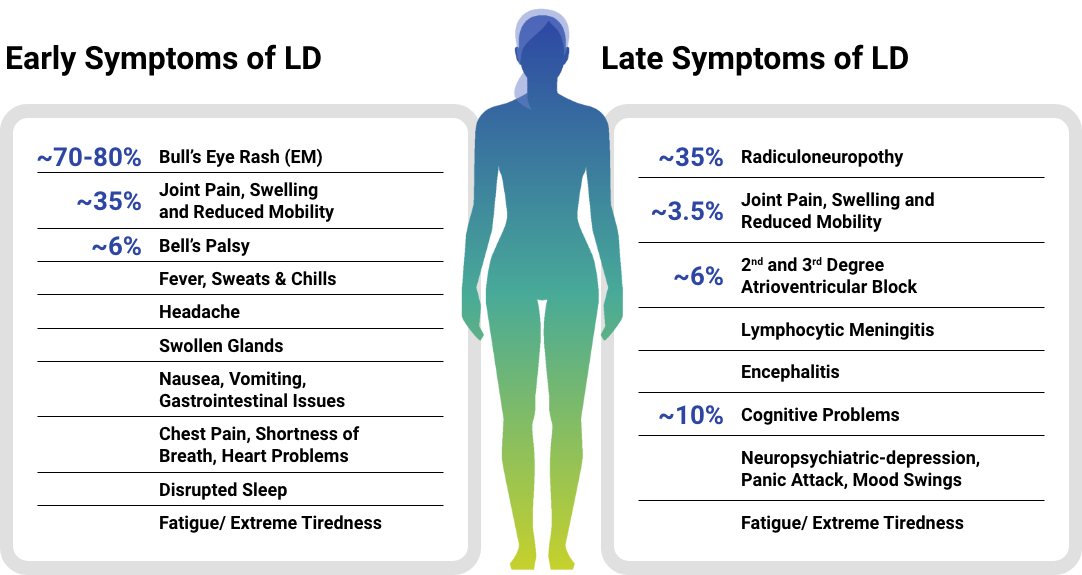
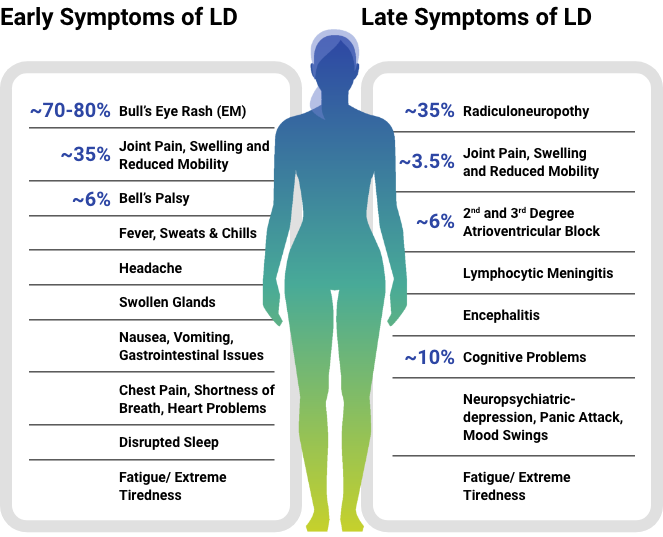

The Diagnosis of Lyme Disease is Often Complicated by Several Factors:

Vague Symptoms:
The symptoms of Lyme disease can be vague and similar to those of other illnesses. Early symptoms of Lyme disease may include fever, headache, fatigue, and a bull’s eye rash, but these symptoms are not always present or easy to recognize. As the disease progresses, symptoms can become more severe and include joint pain, heart palpitations, and neurological problems.
False Negative Tests:
The most common STTT test can produce false negatives if they are administered too soon after the onset of symptoms, or if the patient has been taking antibiotics. Molecular testing for Lyme using PCR is also not recommended since the Borrelia transition rapidly from the blood stream to tissues, and therefore the pathogen load in peripheral blood is insufficient for accurate testing.
Suboptimal Standards of Testing:
There is also debate about the accuracy of these STTT tests, and some experts argue that they may miss up to 50% of cases. This is because the tests are designed to detect antibodies to the bacteria that causes Lyme disease, but not all patients produce enough antibodies to trigger a positive test.
Co-Infections:
Lyme disease can be transmitted by ticks that also carry other diseases, such as Babesiosis, Anaplasmosis, and Powassan virus. These co-infections can complicate the diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease, as they can produce similar symptoms and require different treatments.
Lack of Awareness:
There is a lack of awareness among many healthcare providers about the prevalence of Lyme disease and the need for early diagnosis and treatment. This can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, which can result in more severe symptoms and long-term complications.